
Guide to our Galaxy-0
- Kelvin
The Milky Way, home to our solar system is the second largest galaxy in the local group of galaxies. We are located in the Orion arm.
How many stars are there? - Kelvin
The Milky Way is a normal spiral shape galaxy with a diameter of 120,000 light years. Astronomers predict that our galaxy have more than 400 billion stars! Those stars all come in different shapes and sizes, different colour, different brightness and other awesome features. Some of the 400 billion stars are super giants. They are enormous stars can turn in to black holes and if they ran out of fuel, they burn out. There are ones that are blue, red and even white! One of the examples of these super giants are: VY Canis Majoris (red), Rigel (blue), V533 Carinae (white) and Betelgeuse.
What will our galaxy will be like in the future? - Kelvin
On its own, the Milky Way will not become unstable. It will continue to grow by cannibalizing small galaxies like the Magellanic Clouds* (currently, the Milky Way is swallowing a small dwarf galaxy). Unfortunately, the Andromeda galaxy (which is bigger than the Milky Way) is right now heading towards the Milky Way and will interact or “hit” with our galaxy in billions of years. If we will be able to live by then, the two galaxies will merge and will probably become an elliptical galaxy (like M87). However, these events will take place only after a VERY LONG time.
- Magellanic Clouds are strange looking dwarf galaxies that can be seen in our southern hemisphere.
Interestig facts:#Milky Way Galaxy is a barred spiral galaxy. It has a diameter if about 100,000 light years with more than 100 billion stars.
- A huge supermassive black hole lies in the core of our galaxy.
- Milky Way Galaxy is the second largest galaxy in our group called the "Local Group". Our galaxy is heading towards the largest galaxy in our group, which is the Andromeda Galaxy. This means that we are on a collison course at a speed of about 100 m/s.
- The oldest star in our galaxy is about 13.2 billion years old, which is called HE 1523. It is just younger than our Universe which is 13.7 billion years old. Just to show how old the star is, our Solar System is only 4.6 billion years old.
- Our Sun orbits the Milky Way Galaxy at a speed of 4800 m/s and even at that speed, Our Sun has orbited our Galaxy only 20 times. It takes about 225 - 250 million years for our Sun to orbit the Milky Way Galaxy. This is known as the Galactic Year.
Have any satellites or spacecrafts have landed or passed by your chosen topic? - Justin
The Milky Way galaxy is very large. It would take 100,000 light years to cross the galaxy, something we could never do in our lifetime. The only human made spacecraft to even pass outside our own solar system is Voyager 1. Voyager 1 was launched in 1977; it traveled across our solar system to study the outer planets. Voyager 1 is the f

Above: A photograph of Voyager 1.
astest object ever created by mankind. It pas
sed these gas giants and beyond the heliosphere on September 2013 on its 36th year in space. The heliosphere is the point at which the forces of the solar winds equal the forces of interstellar space, the farthest point of impact our sun has in space. Voyager 1 has only just entered interstellar space and truly started its travel across our galaxy.
What is a Galaxy and what type of galaxy is the Milky Way? - Justin
The Milky Way galaxy, home to our solar system is classified as a spiral galaxy meaning it is a flat rotating galaxy, and the structure forms a spiral spinning from the center out. Other galaxies have different shapes like NGC 6240 a.k.a. the Starfish Galaxy is named after it’s shape that looks like a Starfish. Most large galaxie
s contain supermassive black holes in the center region of a galaxy, while dwarf galaxies do not always. The biggest galaxies are classified as elliptical galaxies and the smallest galaxies are classified as dwarf elliptical galaxies. Galaxies spin around the center region of their galaxy and move through space due to the expansion of the universe and dark energy caused by the big bang. Galaxy is a large gravitational system made of stars, gasses, nebulas, constellations, solar systems, planets, and black holes, quasars, pulsars etc.
What Makes A Galaxy? - Justin
Galaxies made made over time from dwarf galaxies, matter, energy, suns, systems, gases and here are some things that build up a galaxy.
Active Galactic Nucleus Galaxy and Quasars

Above: A photo of a Quasar.
A.G.N. is a region in the center of a galaxy that has a much greater normal luminosity and at least some or possibly all of an electromagnetic spectrum. Quasars are the most distant and hyperactive members of the A.G.N.; they are extremely bright and identified of having electromagnetic energy.
Constellations
Constellations are the area where stars (and sometimes galaxies) are grouped together and create patterns such as gods, animals, and mythical creatures.

Above: A map of some Constellations.
Stars, Novas, Supernovas, Pulsars, Neutron Stars, Binary Stars, and Hyper giants and Planets
Stars are bright spheres of plasma energy that supports its own gravity. In the final days of a suns life, they start to suck in gas and brighten and then explode. Smaller nuclear explosions are classified as Novas, and massive nuclear star explosions are

Carl Sagan observes a supernova explosion Spaceship of the Imagination Remastered
classified as Super Novas and often create a Nebula. Neutron stars are created after a Super Nova explosion. Neutron stars ar

Above: Hyper Giant VY Canis Majoris
e the smallest known stars in the universe but have an immense gravitational pull. A Pulsar is an intensely magnetized, neutron star that emits electromagnetic radiation beams. A binary star is a star system co
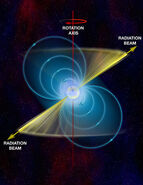
Above: Diagram of a pulsar.
ntaining two stars orbiting around their own center own gravity and mass. Hyper giant stars are the largest classification of stars; hyper giants contain an enormous amount of mass, and are extremely bright. The term planet comes from the ancient Greeks (astēr planētēs meaning: wondering star), a planet is an object orbiting a star that is large enough to be rounded by it’s own common gravity and is apart of the solar systems debris and planet orbit disks.

Above: A diagram of a wormhole.
Black Holes, and Worm Holes.
Black Holes are a region in space which gravity distorts, and prevents everything even light cannot escape the gravitational pull. In the theory of general relativity it pre

Above: A photo of a black hole distorting light
dicts that a certain amount of compact
mass that will deform and distort space-time continuum. Worm Holes are a shortcut through space-time; a wormhole is nothing but a time

Einstein-Rosen bridges - Worm holes, Black Holes
machine teleportation tunnel.
Dark Matter and Energy
Dark Matter is a type of matter in cosmology that no mass can be seen. It does not emit nor absorb light or other electromagnetic radiation. Dark matter is not reactant to light. Dark energy
is a form of energy that expands space and appears to accelerate the expansion of the universe.
How Was Our Galaxy Created? - Justin
Our galaxy, the Milky Way was created around 12 billion years ago after the big bang. Ancient stars from the time after the big bang helped form our galaxy, and remnant from these stars (like gasses create modern stars like our own.) The galaxies also grow by combining with other galaxies and dwarf galaxies and their centers act like cannibals but with black holes.
Is there a special history behind the name of your chosen topic?- Justin
The history behind the name of our spiral galaxy originates back from the ancient Greek times as people watched the sky at night and decided name the galaxy “The Milky Circle” because without lights observing the galaxy looks liken arc or a semi-circle of soft white light. It was only until later in time during the Roman times, people changed the name to “The Milky Road.” The ancient Chinese called the Milky Way the “Silvery River of Heaven” due to it looking like a hazy disk in the night sky. Over time the name was changed and referred by sci
entist as “The Milky Way.” The name Milky came from its looks as it has a dim glowing band arching across the night sky.
Local Group Satellites- Justin
The Milky Way galaxy contains many smaller dwarf galaxies orbiting it like satellites. These dwarf galaxies are part of our galaxies subgroup. The subgroup is part of the Local Group. The Milky Way has in the range of 15 to 30 confirmed dwarf (satellite) galaxies orbiting around it, but some do not orbit and are temporarily fixed in a certain spot in space.
Canis Major Dwarf is the closest dwarf (satellite) galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. It gets it’s name from the constellation it is apart of, Canis Major. It is an irregular galaxy meaning that it does not have a certain and distinct shape like our Milky Way, a spiral galaxy.

Carl Sagan explores the local group of galaxies Spaceship of the Imagination Remastered
Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal galaxy is the second closest dwarf (satellite) galaxy to our Milky Way galaxy. A part of it’s name comes from the constellation it is apart of, Sagittarius. It is an elliptical lopped satellite galaxy orbiting the Milky Way.
Large Magellanic cloud is the third closest galaxy to our own Milky Way galaxy. It is a part of the constellations Dorado and Mensa. It is shaped as a cloud and orbits the Milky Way.

Above: A diagram of Dwarf galaxies orbiting the Milky Way.